Drilling Down on AI in Education
Samsung’s educator survey found that a majority (53%) are already using AI tools in their classrooms, with another 33% exploring possible uses for AI. Among AI applications respondents currently use are interactive learning tools (20%), personalized student learning experiences (22%), and data analysis to gain insights into student performance (11%).
The survey also revealed a range of teacher concerns about AI in education. These include plagiarism (20%), insufficient training on AI education tools (15%), the potential to spread misinformation (13%), and reduced human interaction in learning (12%). Notably, only 5% of teachers expressed concerns about AI leading to job displacement, indicating a broader focus on the opportunities AI presents for teaching and learning.
Encouragingly, 88% of teachers stressed the importance of educating students on the ethical use of AI, underlining its potential to shape responsible, tech-savvy learners.
STEM Perceptions Improving—but Staffing Shortages Persist
The survey results represent a dramatic shift in teachers’ perceptions across the two years since Samsung Solve for Tomorrow’s first State of STEM Education survey during the 2022/2023 school year. At that crucial post-pandemic inflection point for U.S. education, the survey uncovered a mix of anxiety and concern among STEM educators—65% of whom reported STEM faculty shortages, with 13% describing those shortages as severe. In the new survey, reports of faculty shortages have dropped to 37%, and teachers were generally positive about the support their schools provide for STEM education, with nearly three-quarters (73%) saying STEM receives “strong” (18%) to “some” (55%) support. This represents an increase from our first survey, when 65% of teachers reported that local school boards and communities were “generally supportive” of STEM in their schools.
The new survey’s findings also reflected guarded optimism among educators, and a belief in the positive contributions STEM education is making for student achievement. That optimism is in line with the recent NAEP findings that, nationwide, student performance scores in math generally showed a halt to post-pandemic declines, with some locales even showing improvement (as opposed to generally declining reading scores).
Urgent Need to Modernize STEM Curriculum

The STEM educators surveyed are highly passionate about the value of STEM education in preparing students for the future, with 93% of teachers agreeing that STEM skills are vital for students to flourish as they move into the workforce. Yet only 36% of teachers feel their school’s current STEM curriculum effectively addresses emerging trends such as AI, data science, robotics, automation, and accessible and green technologies.
Entrepreneurship: A Missed Opportunity
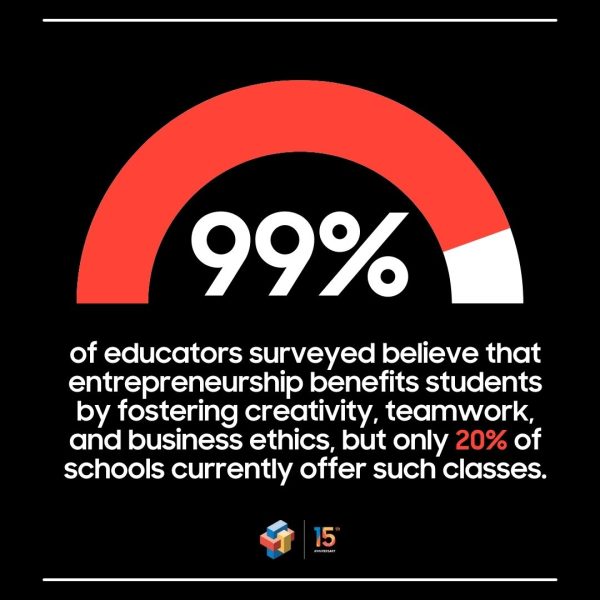
Despite near-unanimous agreement (99%) that entrepreneurship benefits students by fostering creativity, teamwork, and business ethics, only 20% of public middle and high schools currently offer entrepreneurship classes. Teachers overwhelmingly believe such courses would boost student confidence and motivation to pursue innovative careers and social impact initiatives.
By spotlighting the challenges and opportunities in STEM education, Samsung Solve for Tomorrow aims to inspire action among local and state education leaders and community and industry advocates. To learn more about the 2024/2025 STEM competition, which is currently underway, please visit Samsung.com/solve.



